Generative AI is revolutionizing the technological landscape, and its journey can be understood through the lens of generative AI innovation waves. This transformative technology, which creates original content like text, images, and music, is evolving rapidly, unlocking unprecedented opportunities across industries. From its foundational stages to a future where AI proactively guides us, these waves mark significant generative AI advancements. In this article, we’ll explore the four innovation waves, their applications, challenges, and what lies ahead, offering a deep dive into this game-changing technology.
Introduction to Generative AI
Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence that generates new content by learning patterns from vast datasets. Unlike traditional AI, which excels at tasks like classification or prediction, generative AI produces outputs that mimic human creativity—think AI-generated artwork or conversational text. Its significance lies in its ability to amplify human potential, streamline processes, and solve complex problems, making it a cornerstone of modern innovation.
The rise of generative AI innovation waves reflects a progression from basic learning models to sophisticated systems that interact with and even anticipate human needs. This article unpacks these waves, providing insights into their impact and future potential.
The Concept of Innovation Waves
Innovation waves describe the phased evolution of a technology, each wave building on the last to deliver greater capabilities. For generative AI, these waves chart its journey from foundational algorithms to a proactive partner in human endeavors. Understanding these generative AI innovation waves helps us grasp how this technology is reshaping industries and society.
The four waves we’ll explore are: Classification and Training, Generative AI, Interactive AI, and AI Prompting Us. Each represents a leap forward in generative AI advancements, with unique technologies, applications, and challenges.
Wave 1: Classification and Training
Overview of Wave 1
The first of the generative AI innovation waves focused on building AI that could classify data and learn from it. This wave introduced models like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), trained on massive datasets to recognize patterns and make predictions. It set the stage for all subsequent AI developments.
Key Technologies in Wave 1
Technologies like CNNs for image recognition and RNNs for sequence processing were pivotal. These models relied on supervised learning, requiring labeled data to refine their accuracy—a critical step in early generative AI advancements.
Applications of Wave 1
This wave powered innovations like medical image analysis, fraud detection in finance, and personalized recommendations in retail. For instance, autonomous vehicles use classification models to interpret sensor data, a testament to Wave 1’s real-world impact.
Challenges in Wave 1
Challenges included the need for vast labeled datasets and the risk of bias in training data. Interpretability was another hurdle—complex models often acted as “black boxes,” making their decisions hard to explain.
“The first wave of AI was about teaching machines to see and think, but it came with the challenge of ensuring they learned fairly and transparently.” – Dr. Jane Smith, AI Researcher
Wave 2: Generative AI
Overview of Wave 2
The second wave, a cornerstone of generative AI innovation waves, shifted AI from analysis to creation. Models like generative adversarial networks (GANs) and transformers enabled AI to produce original content, marking a significant leap in generative AI advancements.
Key Technologies in Wave 2
GANs, with their generator-discriminator duo, and transformer models like GPT-3 revolutionized content creation. These tools learned from data distributions to generate realistic text, images, and more.
Applications of Wave 2
From AI-generated art (e.g., DALL-E) to automated content writing, Wave 2 transformed creative and business sectors. In healthcare, it’s accelerating drug discovery by designing novel molecules—a prime example of generative AI advancements.
Challenges in Wave 2
Quality control remains tricky, as generated content can be flawed or biased. Ethical issues, like deepfakes and copyright disputes, also loom large, demanding robust oversight.
| Wave | Key Technology | Primary Application | Main Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wave 1 | CNNs, RNNs | Classification, Prediction | Data Bias, Interpretability |
| Wave 2 | GANs, Transformers | Content Generation | Quality, Ethical Concerns |
Wave 3: Interactive AI
Overview of Wave 3
The third of the generative AI innovation waves introduced interactive AI, capable of natural language conversations and task execution. Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT exemplify this wave’s conversational prowess.
Key Technologies in Wave 3
LLMs, built on transformer architectures, process and generate human-like text. Their ability to understand context and respond dynamically drives this wave’s generative AI advancements.
Applications of Wave 3
Interactive AI shines in customer service chatbots, virtual tutors, and workplace assistants. It’s also a creative partner, aiding writers and designers with real-time collaboration.
Challenges in Wave 3
Accuracy is a concern—misinformation from AI can mislead users. Privacy and over-reliance are additional risks, necessitating careful design and regulation.
“Interactive AI is like a conversation partner that never sleeps, but we must ensure it speaks the truth.” – Mark Johnson, Tech Innovator
Wave 4: AI Prompting Us
Overview of Wave 4
The fourth wave envisions AI as a proactive guide, anticipating needs and prompting actions. This futuristic stage of generative AI innovation waves is still emerging, built on prior advancements.
Key Technologies in Wave 4
Future models may leverage reinforcement learning and advanced contextual understanding to predict and suggest. These are speculative but rooted in current trends.
Applications of Wave 4
Imagine AI prompting doctors with health alerts, businesses with market strategies, or individuals with daily plans. This wave could redefine decision-making across domains.
Challenges in Wave 4
Balancing proactivity with human autonomy is key. Misjudgments or intrusive suggestions could erode trust, requiring transparency and user control.
Challenges Across Generative AI Innovation Waves
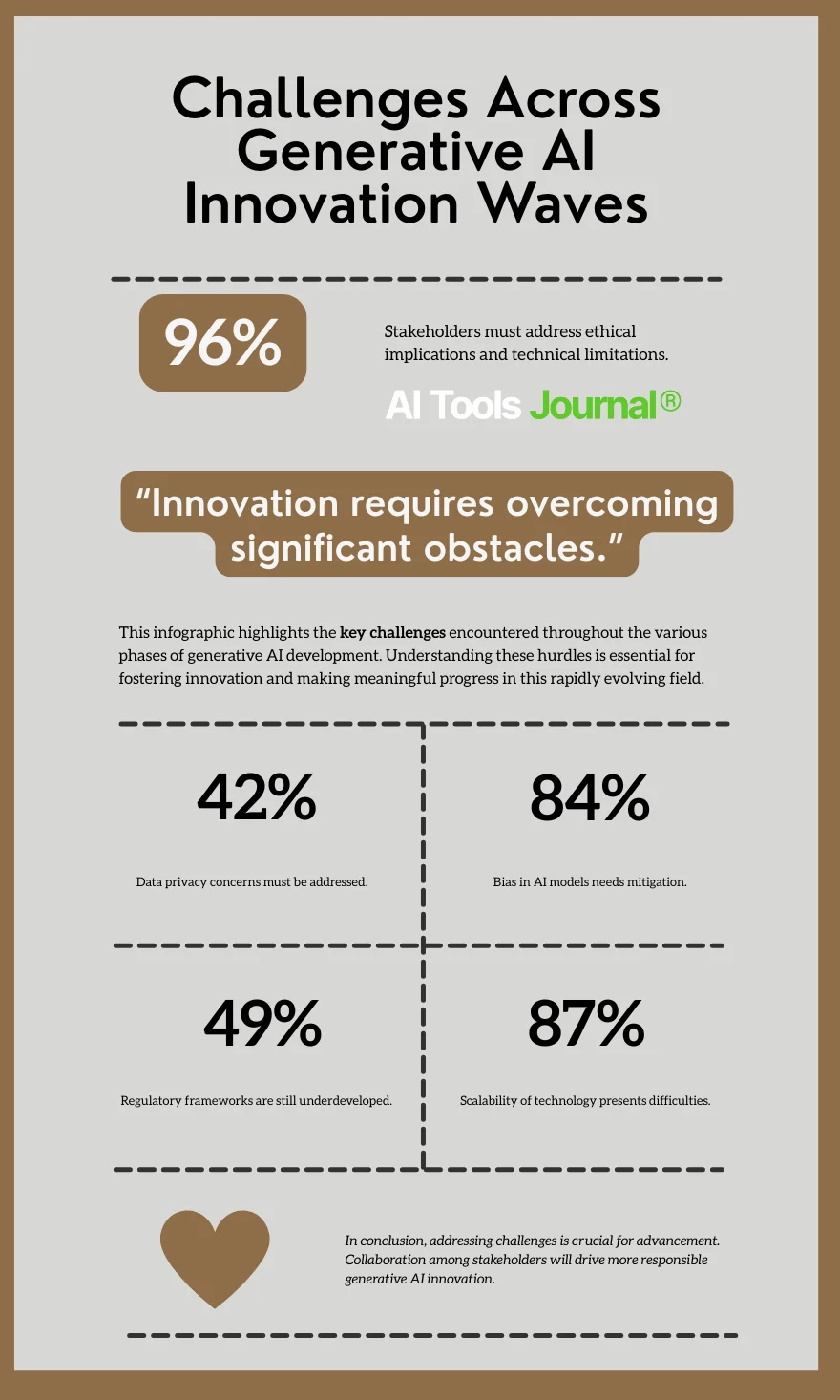
Technical Hurdles
All waves face issues like data demands, computational costs, and output quality. Overcoming these is vital for sustained generative AI advancements.
Ethical Dilemmas
Bias, misinformation, and privacy threats persist across waves. Ethical frameworks must evolve to safeguard society.
Societal Impacts
Job displacement and skill gaps challenge adoption. Addressing these requires education and policy innovation.
Opportunities in Generative AI
Generative AI offers boundless potential—enhancing creativity, solving global issues, and driving economic growth. Collaborative efforts can turn challenges into opportunities.
How Generative AI Works
Core Mechanisms
Generative AI learns data patterns using deep learning. GANs pit a generator against a discriminator, while transformers process sequences with self-attention.
Training Process
Models train on huge datasets, adjusting parameters to minimize errors. This data-intensive process powers their creative output.
Key Algorithms
Algorithms like backpropagation and attention mechanisms underpin generative AI advancements, enabling complex content generation.
The Future of Generative AI Innovation Waves
Looking ahead, generative AI could craft entire experiences—think AI-directed films or real-time scientific breakthroughs. Ethical governance and human-AI balance will shape its trajectory.
“The future of generative AI isn’t just about what it can do, but how we choose to wield it.” – Dr. Emily Chen, Ethics Expert
Conclusion
The generative AI innovation waves—Classification and Training, Generative AI, Interactive AI, and AI Prompting Us—herald a transformative era. Each wave builds on the last, pushing boundaries and redefining possibilities. As we look to the future, embracing these advancements responsibly will unlock their full potential, driving progress while addressing challenges. The new era has dawned—how will we shape it?
FAQs
- What defines generative AI?
Generative AI creates new content by learning from data, distinct from traditional AI’s focus on analysis. - How do the four waves differ?
They progress from learning (Wave 1) to creating (Wave 2), interacting (Wave 3), and guiding (Wave 4). - What’s an example of Wave 2’s impact?
Tools like DALL-E generate art, showcasing generative AI advancements in creativity. - What challenges does Wave 3 face?
Interactive AI struggles with accuracy, privacy, and dependency risks. - What’s next for Wave 4?
AI prompting us could proactively enhance decision-making, pending ethical solutions.






